The Evolution of Business Intelligence: Past, Present, and Future
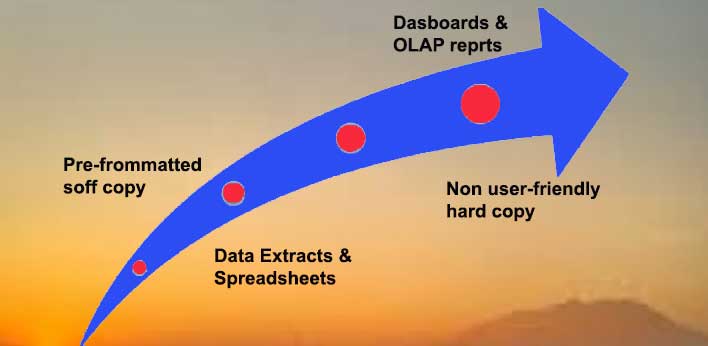
Of course, let’s explore the past evolution of Business Intelligence (BI), its current state, and potential future trends:
Past:
Early Data Processing: BI traces its roots to the early days of data processing in the 1960s and 1970s when organizations began using computers to manage and analyze business data.
These early systems had limited capabilities and primarily focused on basic data storage and retrieval.
Decision Support Systems (DSS): In the 1980s and 1990s, Decision Support Systems emerged, which provided more sophisticated tools for data analysis and reporting.
This system allows companies to make more informed decisions based on data-driven insights.
Data Warehousing: During the same period, the concept of data warehousing became famous. Data warehouses consolidate data from multiple sources, making it easier for organizations to access and analyze information for reporting and decision making.
Present:
Advanced Analytics: Today, BI has evolved significantly thanks to technological advancements. BI tools now incorporate advanced analytics, including predictive and prescriptive analytics, that enable organizations to forecast future trends and determine actions to get better results.
Self-Service BI: Self-service BI has become a prominent trend, allowing business users to access and analyze data without extensive IT involvement. This empowers non-technical staff to create their reports and dashboards.
Big Data Integration: With the development of big data, BI has adapted to handle large amounts of structured and unstructured data. Data lakes and data platforms have emerged as part of the BI ecosystem to support big data analysis.
Data Visualization: Data visualization is becoming increasingly important in BI, with tools like Tableau and Power BI offering interactive and visually appealing ways to present data, making it easier for users to understand complex information.
Future:
AI and Machine Learning: The future of BI will likely be heavily influenced by artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). These technologies will enable BI tools to automate data analysis, uncover hidden insights, and provide real-time recommendations for decision makers.
Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP capabilities will allow users to interact with BI tools using natural language, making it easier for non-technical users to ask questions and receive insights from their data.
Augmented Analytics: Augmented Analytics will become more prevalent, with BI tools automatically suggesting insights, visualizations, and correlations as users explore data, further reducing the barrier to entry in data analysis.
Ethics and Data Governance: As data ethics and privacy considerations continue to grow, BI will need to adapt to increased data governance and compliance features to ensure responsible data use.
Real-time Analytics: The demand for real-time analytics will increase, enabling organizations to make immediate decisions based on the latest data streams from multiple sources.
Personalization: BI systems will become more personalized, providing tailored insights to individual users based on their roles and preferences.
In short, Business Intelligence has come a long way since the beginning of basic data processing. It now includes advanced analytics, self-service capabilities, and integration with new technologies such as AI and NLP.
The future of BI promises greater automation, personalization, and real-time insights to support informed decision making in an increasingly data-driven world.